GCSE CS 1.1 Systems Architecture
What the syllabus says you need to know…
For OCR’s GCSE in Computer Science, Systems Architecture is the first unit you will study. The syllabus below tells you everything you need to know.

Click here to go to the resources
The CPU
What is the role of the CPU?
The purpose of the CPU is to process data. The CPU is where processes such as calculating, sorting and searching take place. Whatever is done on our computers, such as checking emails, playing games, and doing homework, the CPU has processed the data we use.
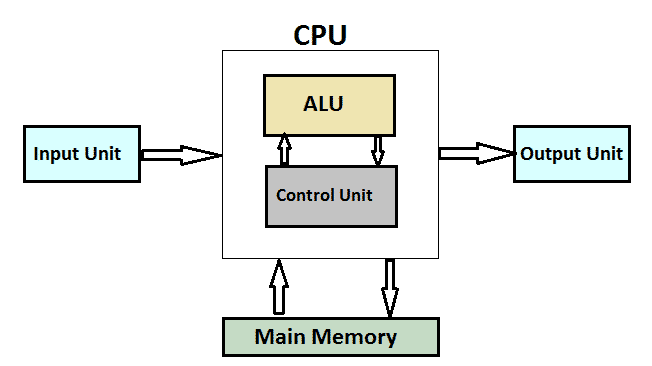
The CPU is made up of three main components, the control unit, the immediate access store, and the arithmetic and logic unit.
The control unit
The control unit controls the flow of data within the system by using signals that monitors the hardware attached to the computer. It controls the input and output of data, checks if things have been delivered successfully, and ensures data gets to the right place at the right time.
A CPU is made up of three parts; the control unit, the arithmetic logic unit, and the registers
Registers are fast pieces of memory that hold all the data and programs in current use. they are like the numbers typed into a calculator – they are being stored inside the calculator while it processes the calculations.
Arithmetic and logic unit
The arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) is where the CPU performs the arithmetic and logic operations. Every task that your computer carries out is completed here. When typing on your computer it needs to calculate the different binary digits in order to be able to change the graphics on your screen to display the words you type.
The ALU’s operations are split into two parts:
- the arithmetic part deals with calculations, eg 1 + 1 = 2
- the logic part deals with logical comparisons, eg 10<3
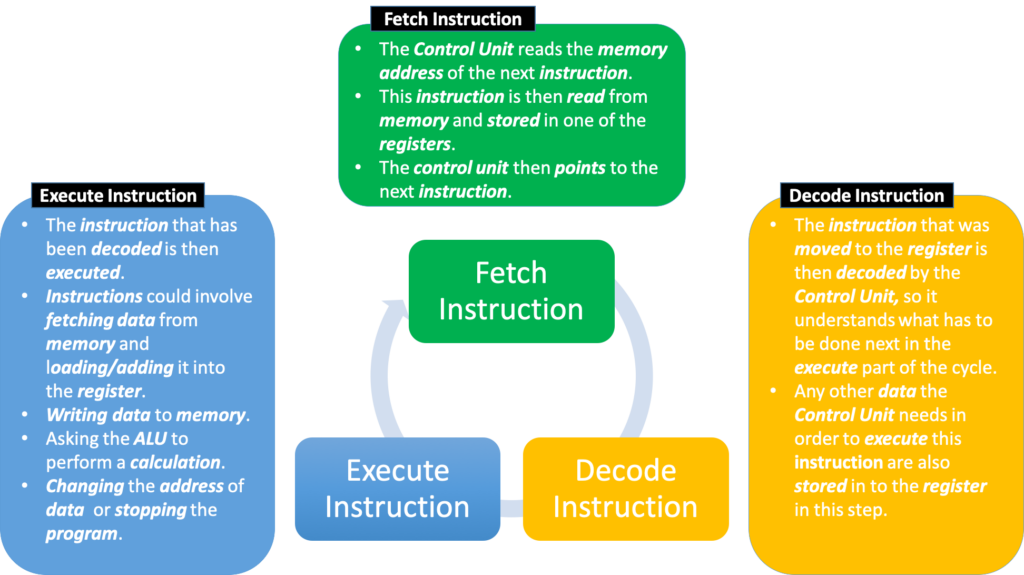
Below is the Fetch Execute Cycle. This is what happens billions of times a second when your computer is running. It is very important to understand each stage and what happens throughout the cycle.

Registers
What are they?
in computer architecture, registers are small but very fast pieces of memory for the processor (CPU) to use. There are several different registers that the processor relies on, however, at GCSE level there are 4 main registers that you must be able to identify and explain their usage of within the CPU.
- PC – Program Counter – stores address of the next instruction in RAM
- MAR – Memory Address Register – stores the address of the next address or next instruction
- MDR – Memory Data Register – stores the data that is to be sent to or fetched from memory
- ACC – Accumulator – stores result of calculations
Outside the syllabus (Extra)
- IR – Interrupt Register – manages requests from I/O devices
- CIR – Current Instruction Register – stores actual instruction that is being decoded and executed

Embedded Systems
What are they?
- A computer system that is made up of both hardware and software: often known as firmware
- Usually for very specialised tasks.
- Doesn’t usually contain an Operating System.
- Single microprocessor including RAM, ROM and a CPU.
An example: Dishwasher.
Their characteristics include:
- They are task specific.
- They do the same task continuously and repeatedly.
- The task is performed in a certain time frame.
- They have a basic or no UI (User Interface).
- Some respond to external stimuli using sensors.

Support Resources
These are external links:
Videos: CraigNDave: 1.1.1 Video, 1.1.2 Video, 1.1.3 Video
Helpful Links/Other:
Lesson Resources
[tml-require-user]
Section 1
- In the first section, you will be learning about the role of the CPU within a computer. You will be able to describe the Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle
- Slides: 1.1.1 The purpose of the CPU
- Workbook: n/a
Extension:
- Exam Questions (ANSWERS)
Section 2
- In this section, you will begin learning about the components of the CPU including the ALU and Cu. You will be able to describe what they do and discuss this in some detail
- Slides: Lesson 2-3 1.1.1 Common CPU Components and their functions
- Workbook: Lesson 2-3
- Homework:
Section 3
- in this series of lessons you will expand on your knowledge of the CPU, understanding the full von Neumann architecure. You will be able to describe the different registers in use as well as the reason for using cache memory. this will link to the factors that can affect the speeds of our CPUs as well as the use of microprocessors used in embedded systems.
- Lesson 4-9 Part 1, Part 2, Part 3
- Part 1 includes the Von Neumann Architecture content,
- Part 2 investigates the common characteristics of the CPU and how they can affects the speed,
- Part 3 explores the use of embedded systems in real world applciations
- Workbook: Lesson 4-9
- Lesson 4-9 Part 1, Part 2, Part 3
Review
Consolidation Lesson (Open PPT)
Don’t look in this area until you have completed the related lesson 😛
Answers to tasks
- Section 1 (n/a)
- Section 2 (n/a)
- Section 3 (n/a)
- Python Code Task
- (Python Code Solution in Github)
Answers to MCQs
- Section 1 (n/a)
- Section 2 (n/a)
- Section 3 (n/a)
Past Exam Questions
Exam Questions and Answers
[else]
You need an account to view this content.

[/tml-require-user]
