IGCSE ICT Chapter 1
Types and Components of Computers
This page will cover Chapter 1 of the IGCSE ICT syllabus by explaining the different types of components that make up our computer systems. Read the syllabus below to get a better understanding of what aspects of the course you need to understand for this unit. You can then read more about the theory further down. If you need teaching resources, click here to skip to them.
What the syllabus says you need to know…
- define hardware, giving examples;
- define software, giving examples;
- describe the difference between hardware and software;
- identify the main components of a general-purpose computer:
- central processing unit (CPU), main/internal memory (including ROM and RAM), input devices, output devices, secondary/backing storage.
- identify operating systems, including:
- graphic user interface (GUI), command-line interface
- identify different types of computer including:
- personal computer (PC) or desktop, mainframe, laptop, palmtop, personal digital assistant (PDA).
The Theory!
This unit focuses on Hardware vs Software. It teaches you what hardware and software are, and the differences between them. Let’s begin…
Hardware
So, what is hardware? it is all the physical components that make up our computing devices. Things like the monitor (screen), the keyboard, and everything inside of the main computer casing.
The main hardware components of a computer are as follows
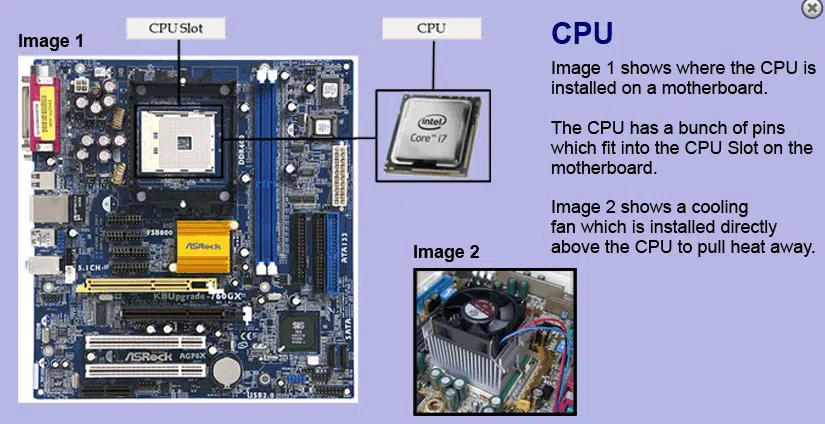
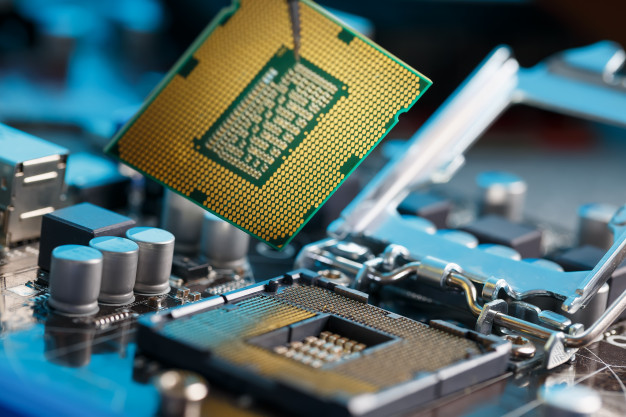
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is like the brain of the computer, it processes and executes all of the instructions of a computer program. It can do basic arithmetic, logic, and controlling other hardware/operations.

Teaching Resources
Restricted
You must be logged in with a premium account to view this content. Click here to visit our shop.

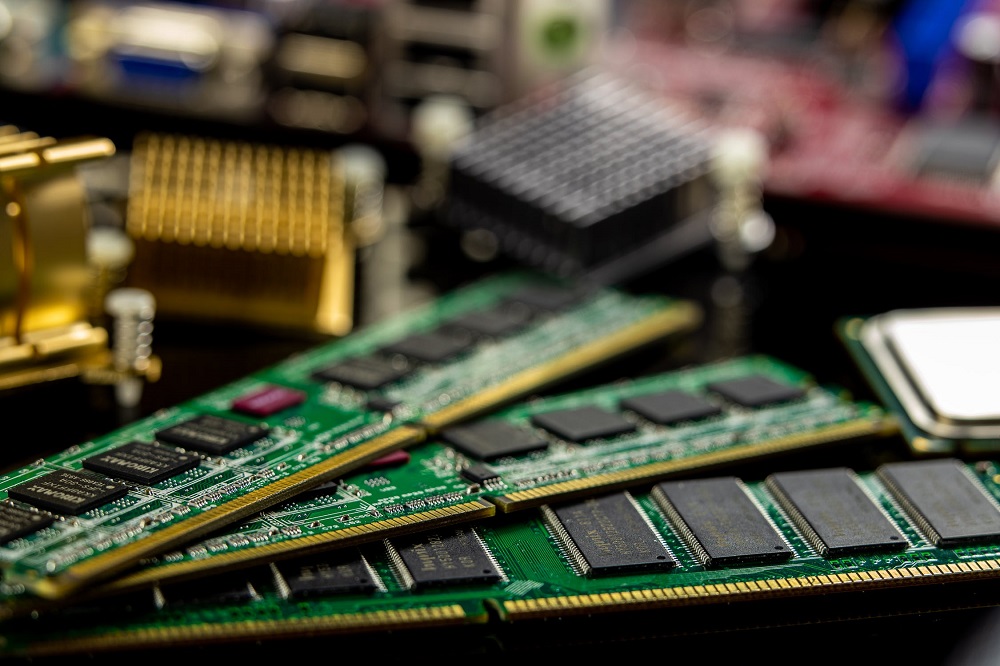
Main Memory (RAM and ROM)
Main memory has two types, Random Access Memory (RAM) or Read-Only Memory (ROM). The difference between the two is the way in which the data is stored. RAM is temporary, volatile memory that stores currently running programs and the Operating System when a computer boots up. ROM is a semi-permanent, non-volatile memory that does not erase the information when it loses power. ROM is used for the BIOS to first boot up the computer.

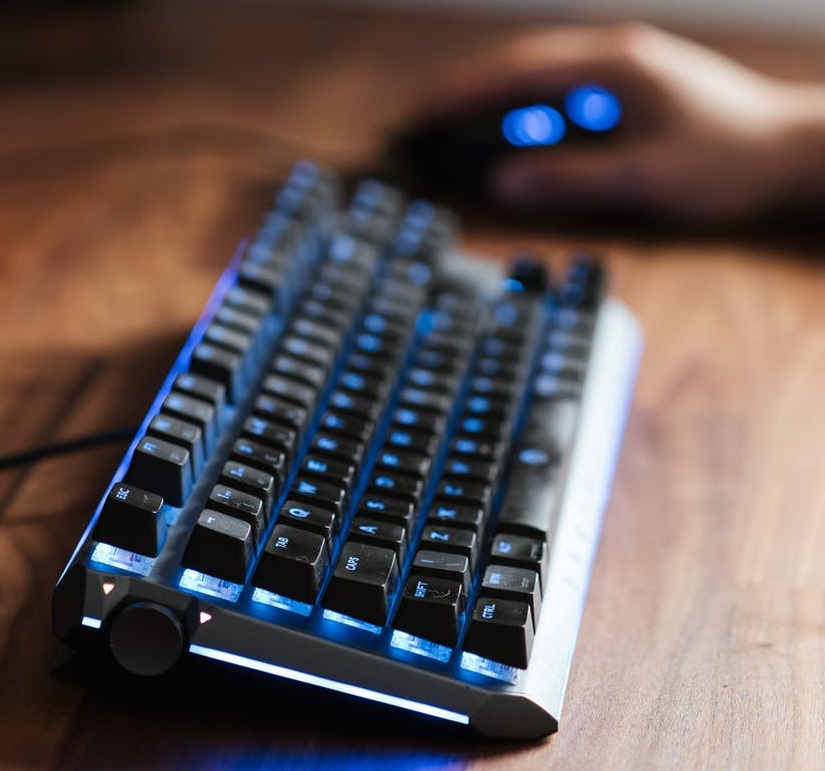
Input Devices
Input devices are hardware components that send information into the computer. Examples include Keyboards, Mice, and Microphones.

Output Devices
Output devices are hardware components that send information out of the computer. These include things like your monitor, printer and speakers.
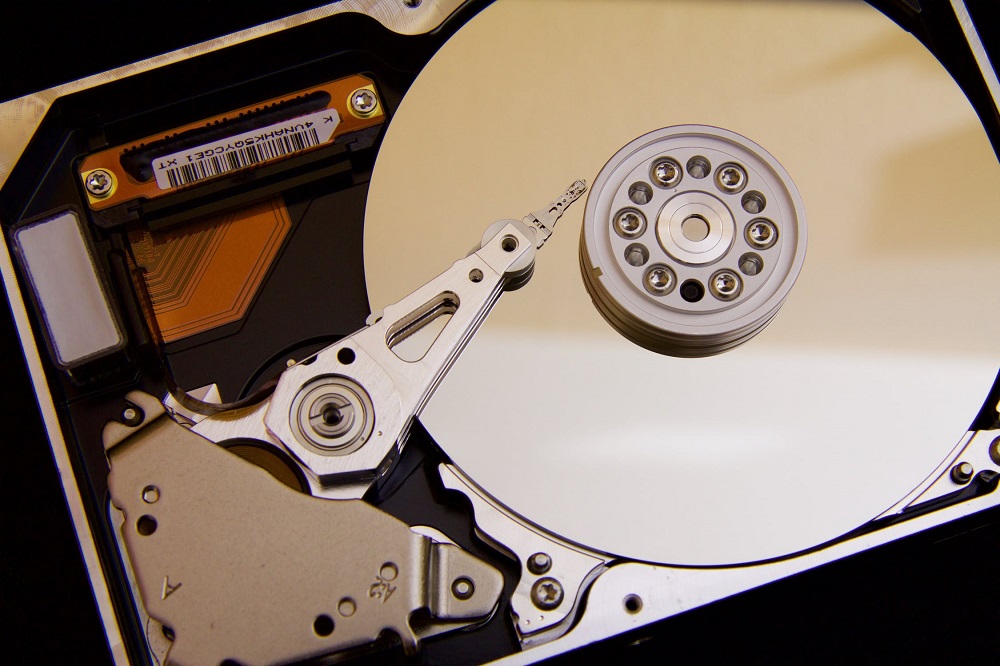
Secondary Storage
Secondary storage is long term storage devices. Examples include HDDs and SSDs. They are used to store your programs and files permanently, unlike RAM. HDDs are Hard Disk Drives, they are generally slower and much cheaper than their newer counterparts, the Solid State Drive (SSD).

Software
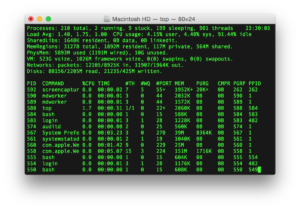
Software is the opposite. These are the instructions or algorithms that run on a computers’ hardware to loan the computer its functionality. They basically make our computer work! There are two main types. One is GUI, or Graphical User Interface, where we use a mouse to navigate the screen and click on windows/icons. A common example would be Microsoft Windows or Apple MacOS. A Command Line Interface on the other hand deals only with keyboard input using a console like an image below. This is generally more powerful than a GUI in terms of the functionality and tasks it can achieve, however, it is not user friendly. GUIs are preferred nowadays by most users do to their ease of use and nice visuals.
Tasks of an Operating System
The Operating System essentially acts as the middle-man between you and your device. It allows you to communicate directly with the hardware by being an interface. People often think about personal computers when anyone says Operating System, but an OS is much more than that. There are many different types of operating systems, and each one of them has different jobs. But if we were to say what an operating system does, in summary, we can bring it down to two main functions. In the image, you can see several tasks that the OS performs.

Types of Computer Systems
Mainframe – a large, expensive computer used primarily by large companies that process a lot of data.
Laptops – smaller, less powerful (relatively speaking) computing devices that have a keyboard, mouse, and screen built-in. They are widely used due to their portability.
Personal Computer / Desktop – a typical computer that is made up of a computer box and a separate monitor. It also has all peripherals connecting externally to it such as the keyboard, mouse and speakers. They are good for home environments.
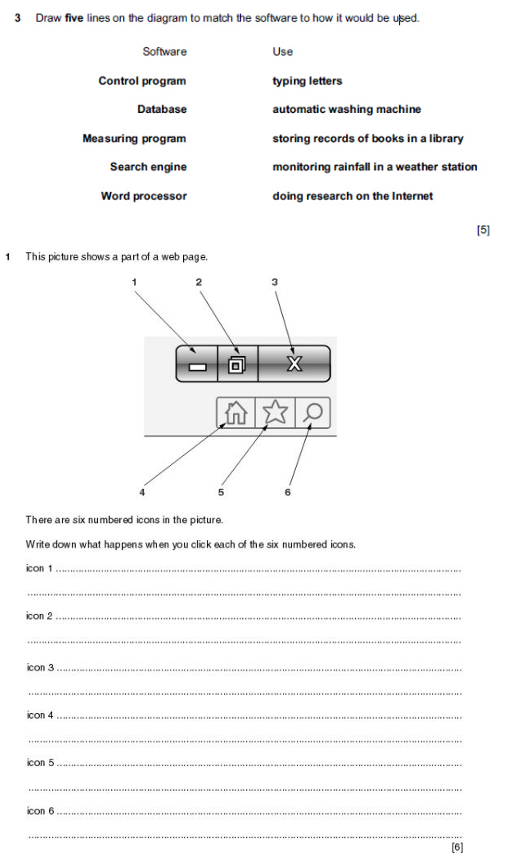
Exam Questions
Complete these in your notebooks as extension activities once you are finished. Did you know, practice exam questions tell students which topics they have not mastered and encourage them to focus on their areas of weakness?