Devices & Infrastructure
5.4 NAT
Network address translation occurs due to a limitation in the IPv4 networking scheme. The interent is a public network and needs a routable IP that is registered. Not all devices can have one – ISPs will provide this to a customer.
The router will assign each device on the internal network with a unique IP that is then converted into a routable IP once it leaves the LAN to go into the WAN.
5.5 VPN
A virtual private network VPN is a remote-access connection that uses encryption
Use IPSec over L2TP – PPTP with MSv2CHAP is insecure!
5.6 Web Threat Protection
Threat types
- – Mass emails
- – Bad links
- – Nefarious websites
Web threat devices;
– save money, time and reportaiton
– hardware-based devices (either All in one / Unified Threat Protection)
– DMZ or internal netowrk
– Policy driven
Types of Protection Devices
Website/URL content filtering – prevents a user from visiting restricted websites. Specific websites are identified as restricted; employees are not able to view the sites on their browsers. Used to enforce the organization’s internet usage policy. Helps to increase bandwidth availability. Does not protect against malcious sites.
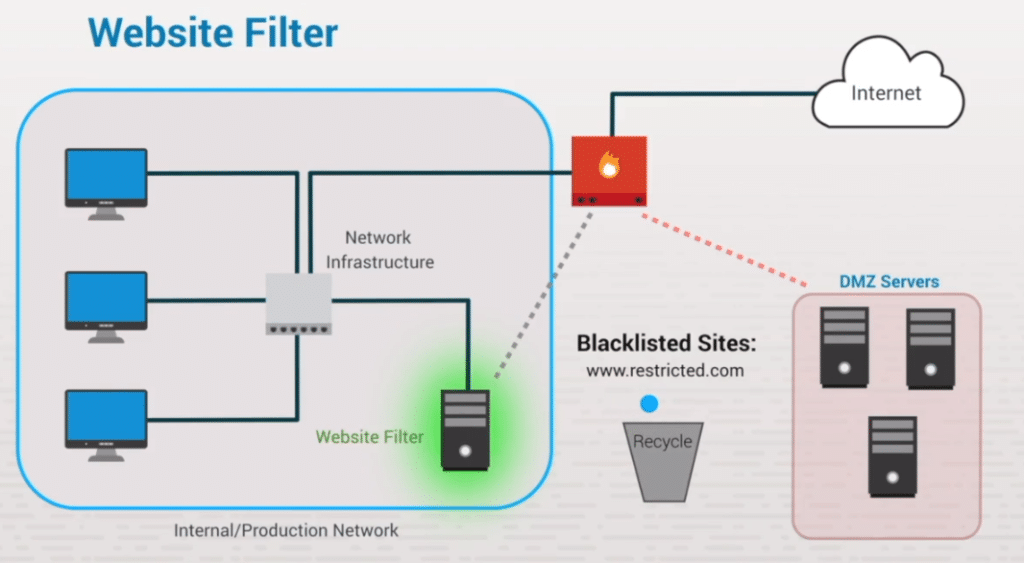
Web threat filtering – prevents a user from visiting websites with known malicious content. It maintains a list of websites with known malicious content.
Gateway email spam filters – prevent spam emails from reaching your network, servers, and computers. Spam filters can be configured to block specific senders, emails containing threats (such as false links), and emails containing specific content.
Virus scanners – identify infected content and dispose of it. Often coupled with email scanners.
Anti-phishing software- scans content to identify and dispose of phishing attempts, preventing outside attempts to access confidential information.
Encryption – causes data, such as the content of an email, to be unintelligible except to those who have the proper key to decrypt it.
Proxies
- Transparent proxies are located between a user and the internet, and they can redirect requests without changing the request.
- Forward proxies can be used to filter web content, but can also be used to mask a user’s identity for anonymity.
- Reverse proxies can be used to direct traffic to internal servers for load-balancing and security
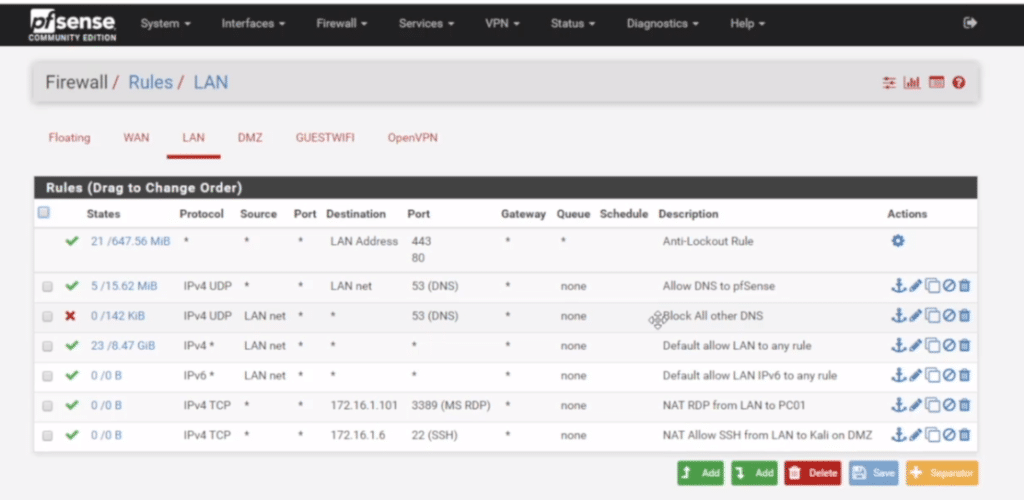
Blocking sites via pfSense
Add packages
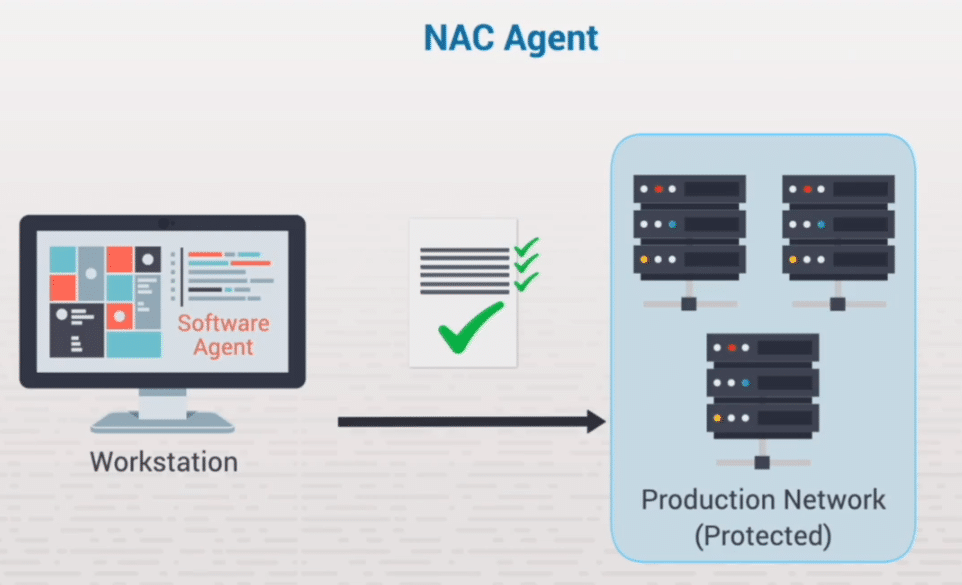
5.7 Network access control
– Network access control – A policy-driven control process that allows or denies network access to devices connecting to a network.
– Bring your own device – A policy that allows an employee to use a personal device, such as a laptop computer or phone, to connect to the organization’s network to accomplish daily work tasks.
Can be used to setup admission criteria to the network – if a device does not satisfy a certain criteria it will be placed onto a restricted network until issues are resolved (device has access to updates and other necessary things to make it conform to the network).
NAC Goals are to prevent zero-day attacks, give role-based controls, encrypt traffic and manage identity / enforce policies.
5.8 Network Threats Facts
Network segmentation
secure network-architecture concept. Idea is that if certain parts of a system are compromised, then the rest of the network is okay. Makes it much easier to identify suspicious network traffic.
Most common method is to setup VLANS (Virtual Local Area Networks) – separate these into zones (low, medium, high), etc. Example of a low-trust zone could be a web server. This kind of zone is also referred to as a DMZ, or demilitarized zone.
Types of network attack
– Active : are when perpetrators attempt to compromise or affect the operations of a system in some way.
– Passive : occur when perpetrators attempt to gather information without affecting the flow of that information from the targeted network.
– External
– Inside : people inside the network security perimeter
User Education and Training
training is very important – phishing is a big concern, therefore educating an organisations employees is beneficial.
Threat focus points
– Entry points – recogonise possible entry points for attacks. Public servers, WIFI, personal devices tc.
– Inherent vulnerabilities – systems that lack proper security controls (older versions of Windows / other SW)
– Documentation – document all asssets to ensure you are securing ===EVERYTHING===.
– Network baseline – identify a normal pattern of usage (server load, net activity etc) so you can detect anomolies or atypical usage.

5.9 Network Device Vulnerability
Attackers try to exploit potential vulnerabilities that you might not even know you have.
***Misconfigured devices***
– Attack surface increase
– Firewalls
– Anti-spam/malware
– WAPs
5.11 Using and configuring VLANs
A virtual LAN can be defined as:
- A logical collection of devices that belong together and act as if they are connected to the same wire or physical switch.
- A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria, rather than physical proximity.
Advantages
VLANs implemented with switches provide several administrative advantages:
- Flexibility in Grouping: VLANs allow the creation of virtual LANs based on various criteria beyond physical location, such as workgroup, protocol, or service.
- Simplified Device Moves: Moving devices to different VLANs becomes effortless by adjusting the port assignments on the switches.
- Broadcast Control and Collision Domains: Logical criteria can be employed to control broadcast traffic and create collision domains, enhancing network efficiency.
- Enhanced Security: VLANs enable traffic isolation, bolstering security by segregating data within specific VLANs.
- Efficient Network Traffic Management: Network traffic can be logically divided and load-balanced within VLANs, providing a more streamlined approach compared to physical segregation.
In comparison to using routers to create distinct networks, implementing VLANs with switches offers the following benefits:
- Ease of Administration: VLANs on switches are simpler to manage compared to configuring multiple distinct networks on routers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Switches are generally more cost-effective than routers, making VLAN implementation a budget-friendly option.
- Higher Performance: Switches introduce lower latency, resulting in improved network performance compared to routing traffic between separate networks.
Disadvantages
- Tied to a specific vendor. Can vary from vendor to vendor making setup more difficult.
- Using VLANs coiuld limit you to one specific vendor throughout the organsiation.
- despite advantages in switches, routers a still required for filtering WAN traffic, routing across VLANs and between different networks.
VLANs and Voice over IP
VLANs are commonly used with VOIP traffic. This allows administrators to distinguish between data and voice traffic as well as set higher priorities for voice traffic to ensure timely delivery.
Configuring VLANs
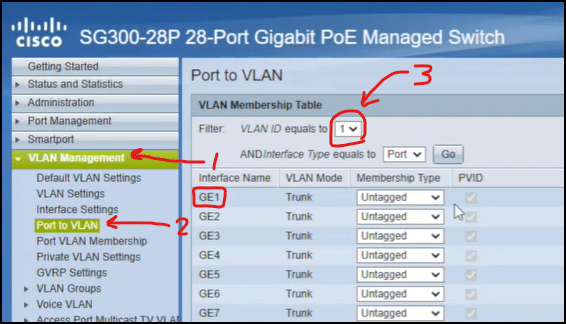
Change the tag for VLAN by and set the “Membership type” to Untagged. This will exclude it from the other VLAN. Shown below.
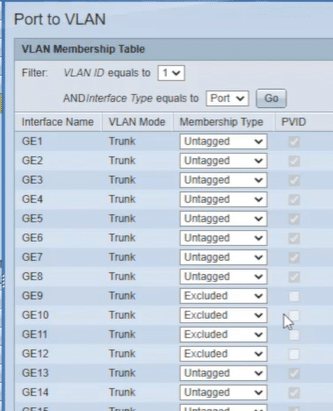
Now you can see on VLAN 1 we have ports 6-9 and “Excluded” meaning they can now function as a separate network (VLAN 2) on the switch as if it were its own.