IGCSE ICT Chapter 3
Storage Devices
This page will cover Chapter 3 of the IGCSE ICT syllabus by identifying storage devices, their associated media and their uses. It will also describe the advantages and disadvantages of devices such as hard drives, CDs, DVDs and Solid State Drives (SSD). Read the syllabus below to get a better understanding of what aspects of the course you need to understand for this unit. You can then read more about the theory further down. If you need teaching resources, click here to skip to them.
What the syllabus says you need to know for this chapter
- identify storage devices, their associated media and their uses, e.g.
- magnetic backing storage media: fixed hard disks and drives, portable and removable hard disks,
- portable and removable hard drives, magnetic tape drives and magnetic tapes, memory cards
- optical backing storage media (CD/DVD/Blu-ray): CD ROM/DVD ROM, CD R/DVD R, CD RW/DVD RW, DVD RAM, Blu-ray discs
- solid state backing storage: solid state drives (SSDs), flash drives (pen drive/memory stick/USB stick)
- describe the advantages and disadvantages of the above devices


Teaching Resources
Restricted
You must be logged in with a premium account to view this content. Click here to visit our shop.

More Information
There are many types of storage devices that can be used in our computer systems. Nowadays, they can be categorised into 4 main areas, listed below:
Magnetic Storage
The oldest type of storage. Includes things like HDD (Hard Disk Drive), Floppy Disk and Magnetic Tape. A hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile storage medium. Non-volatile data remains on a given device unless rewritten or deleted. Magnetic tapes are used as Backup mediums, they feature higher storage capacities than hard disk drives, and they’re more reliable.
Flash Storage
includes things like Solid State Drives (SSD), Flash Drives and SD Cards which contains microchips using NAND flash memory. Generally, these are far superior in terms of transfer speeds. Flashdrives are designed to be portable, pocketable storage solutions.
Optical Storage
Including things like CDs, DVDs and Blu-Ray. These use optical lasers to ‘burn’ or encode binary information into circular disks.
Online Storage
This includes things like Microsoft’s ‘OneDrive’ or Google Drive
Want to know more? Check put this site, here.

A. Magnetic Storage
- How it Works: Uses magnetic fields to represent binary data (0s and 1s).
- Examples: Hard disk drives (HDDs), portable hard drives, magnetic tapes.
- Uses: General-purpose storage, backups, archiving large volumes of data.
- Advantages: Large capacity, relatively fast access (especially HDDs), cost-effective for bulk storage.
- Disadvantages: Moving parts make them vulnerable to damage, slower than SSDs, magnetic fields can cause data loss.
B. Optical Storage
- How it Works: Uses lasers to burn patterns into the surface of a disc, creating pits and lands that represent data.
- Examples: CD, DVD, Blu-ray.
- Uses: Audio/video storage, software distribution, backups.
- Advantages: Affordable, portable, widely compatible.
- Disadvantages: Lower capacity than magnetic and solid state, susceptible to scratches, slower access speeds.
C. Solid State Storage
- How it Works: Stores data using electronic circuits, with no moving parts.
- Examples: Solid state drives (SSD), USB memory sticks, SD cards.
- Uses: Fast internal storage, portable data transfer, cameras, smartphones.
- Advantages: Fast access speeds, durable, portable, no moving parts.
- Disadvantages: More expensive per GB, limited write cycles (especially for USB sticks and SD cards).
Typical Uses and Access Types
- Magnetic Tape: Used for backups and archives; uses serial (sequential) access, which is slow but efficient for large, infrequently accessed data.
- Hard Disk Drives: Used for operating systems, applications, and files; uses direct (random) access, allowing quick retrieval of data.
- Optical Discs: Used for media distribution and backups; mostly direct access, but slower than hard drives.
- Solid State Devices: Used for fast storage and transfer; direct access, very quick read/write speeds.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
| Device/Media | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Disk Drive | Large capacity, fast access | Vulnerable to shock, moving parts |
| Magnetic Tape | High capacity, low cost | Slow, sequential access, vulnerable to magnets |
| CD/DVD/Blu-ray | Cheap, portable, widely compatible | Low capacity, easily scratched, slower access |
| SSD | Very fast, durable, no moving parts | Expensive, limited write cycles |
| USB Stick/SD Card | Small, portable, fast | Easy to lose, expensive per GB |
Backups and the Need for Backing Storage
- Backup: The process of copying files to a different location (disk, tape, cloud, etc.) to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, corruption, accidental deletion, or security breaches.
- Backing Storage vs. Main Memory:
- Main/Internal Memory (RAM): Volatile, fast, temporary storage used while the computer is running.
- Backing Storage: Non-volatile, permanent, used for long-term storage of data and programs.
Key Terms
- Backing Storage: Another term for secondary storage; refers to any non-volatile device used to store data when not in use by RAM.
- Serial/Sequential Access: Data is accessed in order, from beginning to end (e.g., magnetic tape).
- Direct/Random Access: Data can be accessed directly at any point (e.g., hard drives, SSDs, CDs)
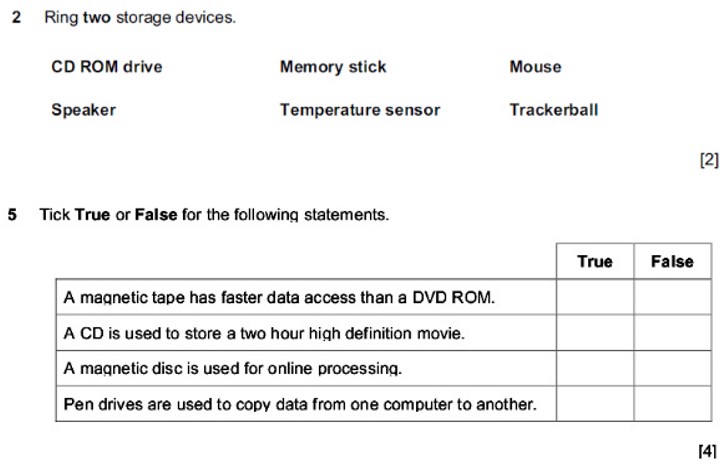
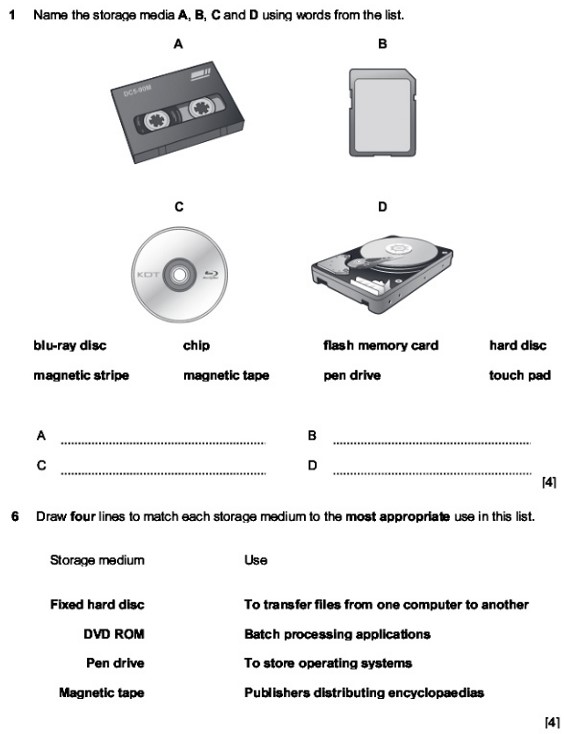
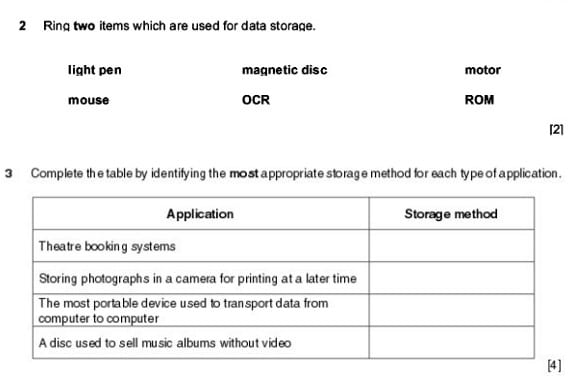
Exam Questions
Complete these in your notebooks as extension activities once you are finished. Did you know, practice exam questions will tell you topics you have mastered along with providing you with an insight into the types and structures of questions you are likely to receive in your exams?